How to Use an ONT in a Fiber Network: A Beginner’s Guide
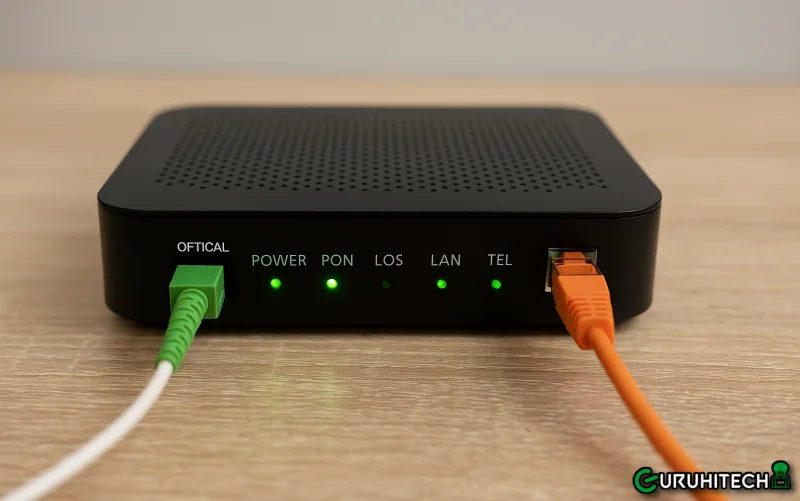

As fiber-optic internet becomes more widely available, the Optical Network Terminal (ONT) has become an essential component in homes and businesses that rely on high-speed broadband. Although the device appears simple, it performs a critical function in delivering fiber internet services reliably and efficiently. Understanding how to install, operate, and maintain an ONT is key for service providers, technicians, and end-users alike.
What Is an ONT and Why It Matters
An ONT (Optical Network Terminal) serves as the endpoint device in a Passive Optical Network (PON). Located at the user’s premises, it connects directly to the fiber optic line provided by the Internet Service Provider (ISP). The ONT’s core responsibility is to receive optical signals from the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) at the provider’s end and convert them into electrical signals. These can then be used by devices such as routers, personal computers, IP phones, and smart TVs.
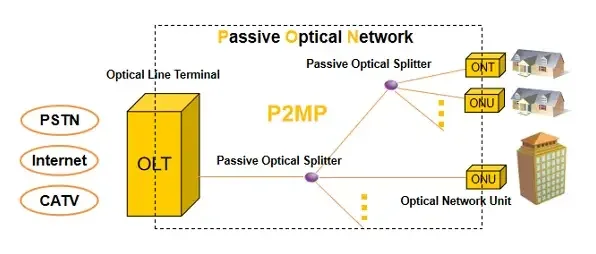
Beyond basic signal conversion, ONTs are often integrated with additional functions like Wi-Fi broadcasting, VoIP (Voice over IP) ports, or CATV RF outputs. This makes them highly versatile in both residential and enterprise networking environments.

Key Functions of the ONT
ONTs play multiple roles in enabling and optimizing fiber internet delivery. Some of their key functions include:
- Signal Conversion: Converts high-speed optical signals into usable digital Ethernet output.
- Device Interface: Provides ports for Ethernet (RJ45), voice (RJ11), CATV (RF), USB, and sometimes built-in Wi-Fi.
- User Authentication: Works with the OLT to authenticate users via serial number, password, or MAC address.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Enables prioritization of traffic, such as voice or video streams.
These functions vary based on the type and configuration of the ONT. Basic bridge ONTs focus purely on data conversion, while gateway ONTs may offer full routing, firewall, and wireless capabilities.
Where and How the ONT Is Installed
A well-installed ONT is essential for a stable and high-performing fiber connection. Typically, an ONT is placed close to where the fiber enters the premises. For residential users, this could be a utility closet, basement, or near a main living area. In multi-dwelling units (MDUs) or businesses, the ONT may be mounted on structured panels or installed in IT racks.
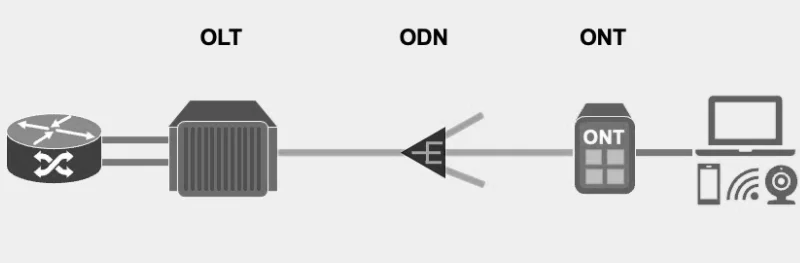
Basic Installation Steps:
1. Connect Fiber Cable: Insert the optical fiber into the ONT’s optical port. Ensure connectors are clean to avoid signal loss.
2. Power Up: Plug the ONT into an AC outlet using the provided adapter.
3. Connect to Router: Use an Ethernet cable to link the ONT’s LAN port to the router’s WAN port.
4. Activate via ISP: Activation may require a serial number, barcode scan, or auto-discovery mechanism.
5. Check Indicators: Verify LED status for Power, PON, LOS, LAN, and Wi-Fi (if applicable).
A proper installation ensures long-term performance and minimizes troubleshooting needs later on.
ONT Troubleshooting and LED Indicators
ONTs come equipped with a set of LED lights that communicate system status and signal conditions. Understanding these indicators is critical for quick diagnostics.
| LED | Status | Meaning |
| Power | On | Device is powered correctly |
| PON | On/Green | Successfully connected to OLT |
| LOS | Blinking Red | No signal or fiber cut detected |
| LAN | Blinking | Data is being transmitted |
| WLAN | On/Off | Indicates Wi-Fi status (if present) |
Common Issues and Fixes:
- LOS Blinking: Indicates a fiber cut or disconnection. Check the fiber for bends or connector issues.
- No LAN Signal: Try rebooting the router or replacing the Ethernet cable.
- No Power: Test another outlet or replace the power adapter.
Pro Tip: Always use dust caps on optical ports and connectors when unplugged to prevent dust contamination.
Best Practices for ONT Performance
To ensure the ONT continues delivering high-speed, low-latency service, follow these best practices:
- Proper Ventilation: Keep the ONT in an open, well-ventilated area to avoid overheating.
- Use Quality Fiber Components: Low-quality pigtails or connectors can significantly degrade signal performance.
- Secure Fiber Lines: Avoid bending or pulling the fiber cable; maintain gentle curves.
- Power Protection: Use a surge protector or UPS system to prevent outages during power fluctuations.
- Labeling and Documentation: Label cables and document serial numbers, especially in enterprise environments.
These steps reduce the likelihood of disruptions and simplify maintenance or future upgrades.
ONT in Different Network Scenarios
ONT deployment and usage vary depending on the environment. Here’s how ONTs are typically used:
Residential Installations
Home users often receive Wi-Fi-enabled ONTs directly from their ISP. These all-in-one devices provide Ethernet, VoIP, and IPTV outputs, eliminating the need for additional hardware. A web interface usually allows basic settings adjustment, such as Wi-Fi passwords and parental controls.
Small Business Deployments
Business-class ONTs offer more robust features like VLAN configuration, static IP assignment, and support for power backup solutions. These ONTs may be integrated into server racks and used alongside managed switches or security firewalls.
ISP Deployments
ISPs manage thousands of ONTs at the neighborhood or city level. Centralized platforms like Element Management Systems (EMS) or Network Management Systems (NMS) allow remote monitoring, provisioning, firmware upgrades, and alarm reporting. Effective ONT fleet management helps ISPs deliver consistent service and respond proactively to faults.
Maintaining and Replacing an ONT
ONTs typically have a long lifespan but do benefit from routine checks. Over time, environmental conditions like dust or high heat can affect performance. ISPs often schedule ONT replacements every 5–7 years or when newer standards like XGS-PON are introduced.
For End-Users: Contact your ISP if performance drops or connectivity becomes unstable. A technician can test the signal and recommend a replacement if necessary. When replacing the ONT, make sure it is compatible with your network and properly registered with the ISP’s OLT.
Conclusion
The ONT plays a vital role in ensuring the end-user receives fast, stable internet from a fiber network. From installation to troubleshooting and optimization, understanding how this device works empowers users and technicians to achieve better connectivity outcomes. Whether for home streaming, small business operations, or ISP-level deployments, a well-managed ONT is the gateway to seamless, high-speed broadband experiences.
Ti potrebbe interessare:
Segui guruhitech su:
- Google News: bit.ly/gurugooglenews
- Telegram: t.me/guruhitech
- X (Twitter): x.com/guruhitech1
- Bluesky: bsky.app/profile/guruhitech.bsky.social
- GETTR: gettr.com/user/guruhitech
- Rumble: rumble.com/user/guruhitech
- VKontakte: vk.com/guruhitech
- MeWe: mewe.com/i/guruhitech
- Skype: live:.cid.d4cf3836b772da8a
- WhatsApp: bit.ly/whatsappguruhitech
Esprimi il tuo parere!
Ti è stato utile questo articolo? Lascia un commento nell’apposita sezione che trovi più in basso e se ti va, iscriviti alla newsletter.
Per qualsiasi domanda, informazione o assistenza nel mondo della tecnologia, puoi inviare una email all’indirizzo [email protected].
Scopri di più da GuruHiTech
Abbonati per ricevere gli ultimi articoli inviati alla tua e-mail.
